What is Noopept?
Noopept is a synthetic nootropic substance with effects very similar to piracetam.
Noopept is much more potent than piracetam or other racetam nootropics and requires a dosage about a hundred times smaller (10-40 mg compared to 4800 mg for piracetam).
This synthetic nootropic was created in 1996 and is now one of the most popular nootropic substances on the market. Its incredible potency, high level of safety, and effectiveness towards supporting focus and concentration make it a perfect addition to nootropic stacks and formulas.
New to nootropics? Check out this Introduction to Nootropics!
Where Does Noopept Come From?
Noopept (aka GV S-111) is a synthetic nootropic molecule created in 1996. The patent for this compound is currently held by a company in Russia.
The compound is created in a lab and distributed throughout the world under the brand name Noopept.
+ Benefits
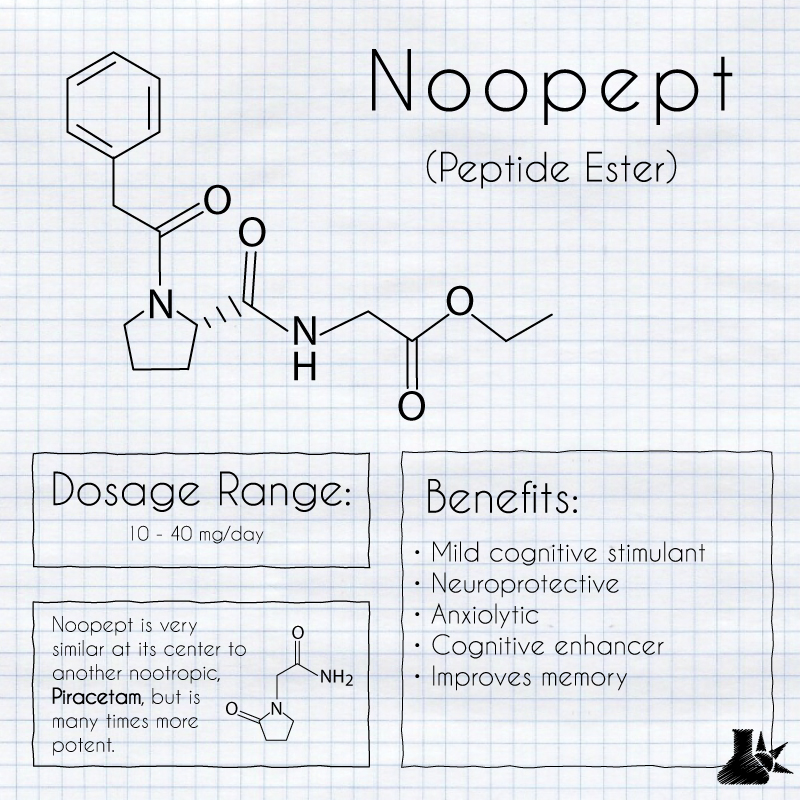
- Improves memory
- Increases creative workflow
- Protection from neurological damage
- Increase efficiency during work or study
+ Mechanisms
- NMDA receptor modulator
- Cholinosensitizing agent (speculative) [6]
Noopept Actions:
- Cognitive Stimulant (Mild)
- Neuroprotective
- Anxiolytic
Dosage
10 - 40 mg/day
Learn MoreChemical Description of Noopept:
Noopept is the brand name for N-phenylacetyl-L-prolylglycine ethyl ester. It is commonly grouped together in the racetam family but lacks the 2-oxo-pyrollidine skeleton that defines racetams.
Noopept is based on the endogenous neuropeptide cycloprolylglycine [2]. It's a dipeptide conjugate of Piracetam.
How Does Noopept Work?
Noopept crosses the gastrointestinal tract with a Tmax of 0.116 hours which is equivalent to 7 minutes. It reaches a Cmax of 0.82 mcg/mL in blood serum in rats. The dose used to determine this was 50 mg/kg but was reported to be nearly identical to a 5 mg/kg dosage. Measurements taken both in the brain and in systemic blood circulation were almost identical, suggesting that noopept can easily cross the blood-brain barrier. [3].
The half-life of noopept in rats was found to be approximately 16 minutes in rats and undetectable after 25 minutes. This doesn't consider cycloprolylglycine, which is believed to be an active metabolite. [3]. Changes in brain wave function are noted to last over 70 minutes, indicating the metabolites were having a strong, active role in the compound. [4].
The major metabolite of Noopept is the endogenous neuropeptide Cycloprolylglycine (Proline and Glycine in a cyclic configuration). [6].
Pharmacology & Medical Research
+ Memory Enhancement
Single doses and long-term dosing have both been shown to increase NGF, and BDNF mRNA concentrations in the hippocampus (of rats). In the long term study, there appeared to be no development of tolerance, and a greater increase of NGF levels. [6].
Noopept is suggested to have a choline-sensitizing effect in vitro [6].
+ Anxiety
Noopept was shown to produce anxiolytic activity in rats [2].
+ Antidepressant
Noopept has been found to produce antidepressant activities in rat models [8, 9].
Toxicity & Safety of Noopept
The toxicity of noopept is incredibly low. In pre-clinical studies on toxicity, researchers reported "no allergenic, immunotoxic, and mutagen activity" despite 6 months of heavy dosing (100 mg/kg).
This dosage range had no effect on the progeny of the affected mice. [1].
Putting this dose in perspective, a normal dosage of noopept is between 10-40 mg/day for the average adult (~60 kg). That's less than 1% of the tested dosage.
Synergy:
Possible synergy with cholinergics such as the racetams or alpha-GPC.
Recent Blog Posts:
References:
Kovalenko, L. P., Smol'nikova, N. M., Alekseeva, S. V., Nemova, E. P., Sorokina, A. V., Miramedova, M. G., ... & Daugel, D. N. (2001). Preclinical study of noopept toxicity. Eksperimental'naia i klinicheskaia farmakologiia, 65(1), 62-64.
Gudasheva TA, et al Anxiolytic activity of endogenous nootropic dipeptide cycloprolylglycine in elevated plus-maze test . Bull Exp Biol Med. (2001)
Boiko SS, et al Pharmacokinetics of new nootropic acylprolyldipeptide and its penetration across the blood-brain barrier after oral administration . Bull Exp Biol Med. (2000)
Vorobyov V, et al Effects of nootropics on the EEG in conscious rats and their modification by glutamatergic inhibitors . Brain Res Bull. (2011)
Gudasheva TA, et al The major metabolite of dipeptide piracetam analogue GVS-111 in rat brain and its similarity to endogenous neuropeptide cyclo-L-prolylglycine . Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. (1997)
Ostrovskaya RU, et al Noopept stimulates the expression of NGF and BDNF in rat hippocampus . Bull Exp Biol Med. (2008)
Neznamov GG, Teleshova ES Comparative studies of Noopept and piracetam in the treatment of patients with mild cognitive disorders in organic brain diseases of vascular and traumatic origin . Neurosci Behav Physiol. (2009)
Uyanaev AA, Fisenko VP, Khitrov NK Effect of noopept and afobazole on the development of neurosis of learned helplessness in rats . Bull Exp Biol Med. (2003)
Uyanaev AA, Fisenko VP Studies of long-term noopept and afobazol treatment in rats with learned helplessness neurosis . Bull Exp Biol Med. (2006)





As COVID-19 continues to spread around the world, we’re getting a lot of questions on what the potential role of herbal medicine is during the outbreak. Learn how the virus works and how to limit your chances of transmission.